WORLD NEGLECTED PANDEMICS ! PANDEMIC TIMES ?
Forgotten Pandemics
The mobilization and resources devoted to the Influenza 2009 H1N1 Pandemic has overshadowed daily pandemics afflicting poor countries and even some so-called rich countries. It is always difficult to make health choices and select diseases due to budget and resources limitation. During the last decade, AIDS budget has increased at the rate of 48% per year and accounts for almost 50% of health aid provided by rich donor countries. Pneumonia kills 1.8 million young children each year. Diarrhea kills 1.5 million young children per year and lives can be saved by cheap rehydration solution and the disease prevented by Rotavirus vaccine. Yet the global budget for maternal and child health was only $640 million compared to US AIDS budget of $7.4 billion in 2007. UNAIDS a special agency and global fund deal with AIDS. Are we paying attention to Glamorous diseases only. About 80% of the disease burden of the developing countries is due to unsafe and untreated drinking
water. We hope that this pandemic will alert us and we will reflect on the pandemics that currently exist and are forgotten.
Table des matières
LES AUTEURS

The resource mobilization, media attention, astronomical budget (>500 billion dollar) and diversion of healthcare staff devoted to the Pandemic 2009 H1N1 Influenza with relatively low mortality can be considered a success. If the same budget and mobilization is devoted to the the other Pandemics with relatively much higher mortality, many of the diseases mentioned herein can be defeated and millions of lives saved.
WHO and UNICEF have launched a joint appeal to donor countries and NGOs and foundations for $39 billion over the next 6 years to protect children and save 5.3 million lives.
This can be achieved through breast feeding for the first 6 months, children vaccination for Measles, DTP, Hib, Pneomococcus (Prevnar) and rotavirus vaccines( Rotateq, Rotarix) and oral rehydration solution/salts and zinc tablets for children with diarrhea.
In Nigeria and Ethopia deaths of 540000 children were due to diarrhea and pneumonia and 237000 deaths due to AIDS.
USA provided $750 million for AIDS treatment to these 2 countries and 35 million for the maternal and child health. Inspite of increased AIDS budget, only 50% of the patients have access to treatment.
This can be achieved through breast feeding for the first 6 months, children vaccination for Measles, DTP, Hib, Pneomococcus (Prevnar) and rotavirus vaccines( Rotateq, Rotarix) and oral rehydration solution/salts and zinc tablets for children with diarrhea.
In Nigeria and Ethopia deaths of 540000 children were due to diarrhea and pneumonia and 237000 deaths due to AIDS.
USA provided $750 million for AIDS treatment to these 2 countries and 35 million for the maternal and child health. Inspite of increased AIDS budget, only 50% of the patients have access to treatment.
Means of control:
- 2 billion People are exposed each year
- 500 million clinical cases occur each year
- + de 2 million deaths annually
- malaria kills 1 child every 30 seconds in Afrique (WHO estimate)
- Antimalarial drugs
- Fight against mosquitoes
- Use of mosuito nets preferably impregnated with anti-mosquito
Economic Repercussions :
- Causes a decrease ingrowth rate could go up 2%
World Youth Day :
In may 2007 only, as 192 members of the World Health Organization, chose the date of April 25, 2008, to celebrate the first World Day of struggle against the paludisme.The Monde.fr
- April 25 : "One Day to act"
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO on malaria :
"Malaria is preventable and curable"
- Personal Reflection :
Why then 500 million clinical cases and 2 million deaths each year ?

- 2 million people die each year (90% are cildren)
- Particularly affect developin countries
- Rotavirus (virus) alone kill more than 500 000 children under 5 each year cause nearly 5 million hospital (source WHO).
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
insérer des vidéos

Means of control:
The WHO has included HIV / AIDS as the top priority of his interventions.
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Décembre 1
- Reflection of the WHO on malaria :
- Personal Reflection :
- hépatitis B :
- hépatitis C :
Retinal Complications of Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
With a pandemic influenza, seasonal flu can kill more?

Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
- Rehydratation salt solution, ORS or oral rehydration salts
- Breastfeedin : Le lait Maternel : un Nouveau Regard
- Acces to drinking water
- better sanitation
- better housing
- best power
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO on malaria :
She recommends all countries to include vaccine against the virus alone?
- Personal Reflection :
Both vaccines already exist, Rotarix from GlaxoSmithKline and RotaTeq, Sanofi Pasteur MSD, then why not apply the same policy as that will be adopted for influenza A (H1N1) v.
Let us not forget that diarrhea alone represent almost 20% of infant mortality in the world (even developed countries are not immune).She recommends all countries to include vaccine against the virus alone?
- Personal Reflection :
Both vaccines already exist, Rotarix from GlaxoSmithKline and RotaTeq, Sanofi Pasteur MSD, then why not apply the same policy as that will be adopted for influenza A (H1N1) v.
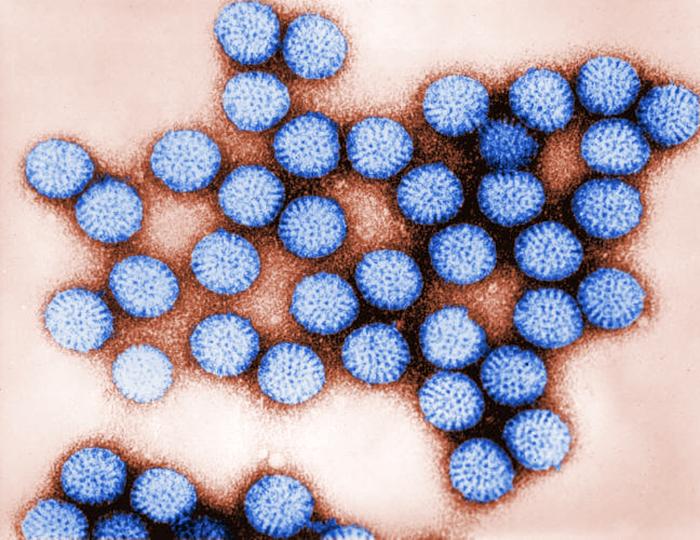
CDC PHIL 178 Electron Micrograph of Rotavirus
- 2 million people die per year (countries most affected developing)
- 700 000 à 1 million, live with AIDS in developing countries (and treatment)
- 7400 new infections each day worldwide or 2.7 million per year (report of March 18, 2009 of the UNAIDS)
- 33.4 million persons living with HIV out of which 22.4 million are in Africa.
- From 1980 to 2008, AIDS has infected 60 million and killed 25 million patients.
- Tritherapy has saved 2.8 million lives mostly in the developed Western countries.

Means of control:
The WHO has included HIV / AIDS as the top priority of his interventions.
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Décembre 1
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO on malaria :
- Personal Reflection :
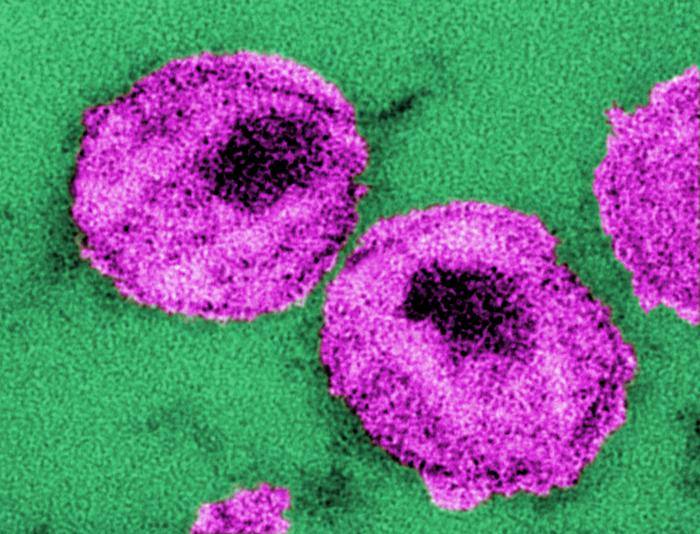
CDC PHIL 10860 Transmission Electron Micrograph of AIDS Virus

 |
| voilà.fr |
 |
| diplomatie.gouv.fr |
- 2 million people die each year (countries most affected developping)
- 2 billion people infected
- 370 million are chonic carriers (thus transmitting the virus and this for years)
- hépatitis C :
- 3 % of world population is affected
- 170 million people chronically infected
- 4 million people are infected each year
 |
| Transmission Electron micrograph of Hepatitis B Virus CDC PHIL ID 11755 |
Retinal Complications of Chronic Hepatitis C Treatment
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
- 2.4 billion people infected each year worlwide (90%, in developing countries)
- 1.8 million deaths per year
- DOTS 6 month treatment costs only $ 20.
- Multi Drug Resistant TB 2 years treatment costs $ 500
- MDR TB 440,000 cases 50% in China, India
- Russia 1 out of 4 TB case is MDR
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
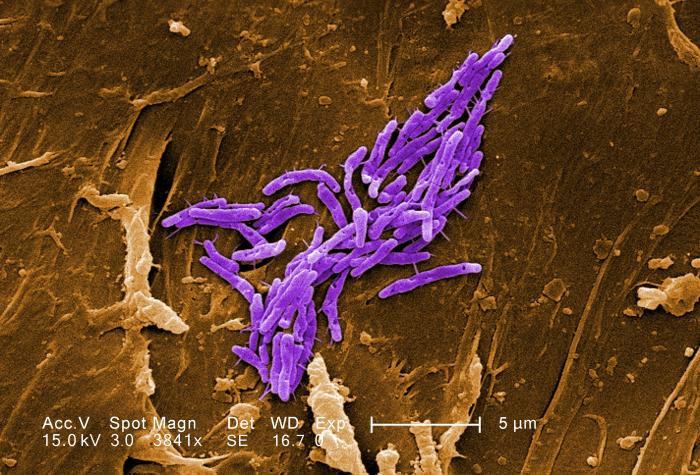 |
| Scanning Electron Micrograph of Mycobacterium CDC Phil ID 11033 |
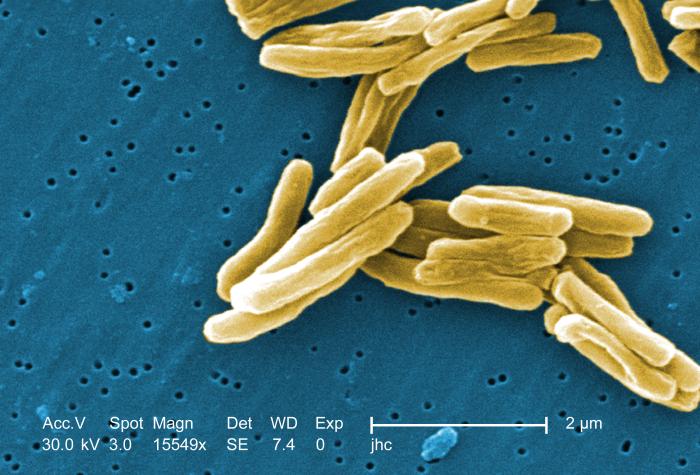 |
| Mycobacterium tuberculosis CDC PHIL 9997 |
- 500 000 people die each year from seasonal influenza
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
With a pandemic influenza, seasonal flu can kill more?
All deaths are being reduced as the influenza A pandemic??
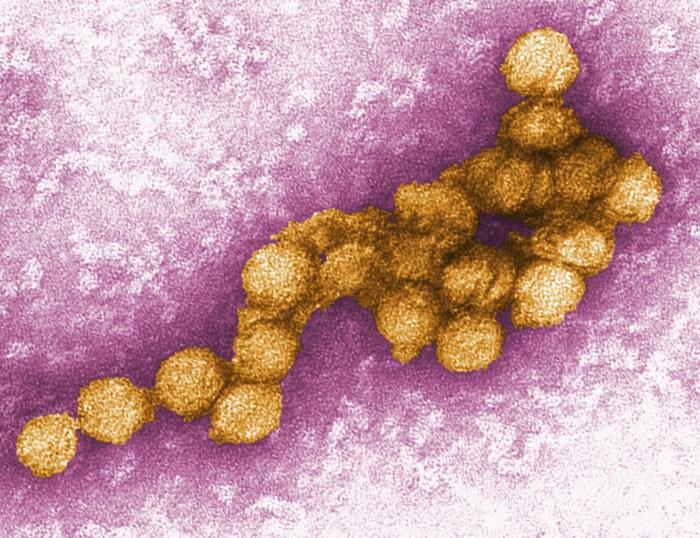
CDC PHIL 11745 This highly-magnified, digitally-colorized transmission electron micrograph (TEM) depicted numbers of virions from a Novel Flu H1N1 isolate.

Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
- Personal Reflection :
- Tuberculose et VIH/SIDA
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
- Malaria and HIV - AIDS
- 1,37 million new cases of TB inpeople infected with HIV
- 456 000 deaths
Means of control:
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
"It is urgent to identify, prevent and treat TB among people living with HIV and to submit to a test for HIV screening all TB patients to ensure prevention, treatment and care.
For this, countries must adopt programs to work more closely and have health systems stronger to fight against both diseases).
- Personal Reflection :
apply, what we do in 6 months for a pandemic that has the name (yet).
Links (do not miss reading):
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2009/tuberculosis_report_20090324/fr/index.html
"It is urgent to identify, prevent and treat TB among people living with HIV and to submit to a test for HIV screening all TB patients to ensure prevention, treatment and care.
For this, countries must adopt programs to work more closely and have health systems stronger to fight against both diseases).
- Personal Reflection :
apply, what we do in 6 months for a pandemic that has the name (yet).
Links (do not miss reading):
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/news/releases/2009/tuberculosis_report_20090324/fr/index.html
- Malaria and HIV - AIDS
Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- Reflection of the WHO :
- Personal Reflection :
- The West Nile Virus
- Ebola
 |
| CDC PHIL ID 10701 Transmission electron Micrograph of West Nile Virus |
- Ebola
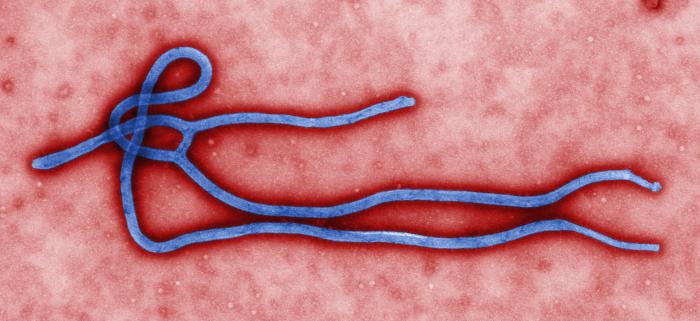 |
| CDC PHIL ID 10816 Transmission Electron Micrograph of Ebola Virus |
- More than 400 millions people are infected worldwide
- Respiratory diseases caused 4.2 million deaths in 2008
- More than 300 millions people are infected wordwide
- More than 900 millions people are infected wordwide
WHO 2008 Strokes and cardiovascular diseases contributed to 17 million deaths worldwide.
- 336 million people have diabetes
- 80% of diabetes deaths occur in countries in developing countries
- 4.6 million deaths were attributed to diabetes in 2010
- 1 billion people suffer from hunger
- 45 000 die each day from malnutrition and diseases associated
- 33 countries are currently affected (sub-Saharan Africa and South-Eastern Asia)
- 86 countries do not themselves enough to feed their populations or can not do
- 2 million people in Ex.Yougoslavie (Serbia, Montenegro), in need of food aid
- 28 million Americans are food insecure
- Sharp rise in food prices during 2007-2008
- Food riots in 36 countries, fall of governments in Haiti and Madgasker
- Statis agricultural yields, decline in agricultuaral aid, opposition to genetic modified high yielding seeds
- stop the wars in poor countries and especially not to sell arms
- Trade must be equitable between rich and poor
- FAO/UN call for $44 billion per year to eliminate hunger has not been funded, vague promises and wasted annual meetings.
One day fast by the FAO and UN highest officials sends a message. FAO appeals for private donations.
Create a Global Fund for Agriculture
Stop infighting and turf protection FAO, WFP, IFAD and CGIAR


Economic Repercussions :
World Youth Day :
Réflexion de l'OMS au sujet du paludisme : World Youth Day :
Reflections :
- paradoxes : the FAO/WHO,the fight against hunger and obesity
Réflexion personnel :
- That western politicians and others, stop supportin the corrupt political regimes and their people that kill them slowly
 |
| URL de cet article sur Tlaxcala : http://www.tlaxcala.es/pp.asp?reference=4991&lg=fr |

(which will be the greatest threat to the species)
3.8 million dead stock of the Vietnam conflict.
- 5 billion people are exposed every day to a war (in the country to democracy without the names, countries of the former Russian bloc, the African countries, South American countries...)
- 250 000 children are currently involved in wars, 60 governments and armed groups using child soldiers (UN sources).
- ...........million deaths (between 1954 and 2008)
- ...........thousnds or millions of missing
- ............million displaced
- ............million refugees
- .............700-800 million persons with disability, 80% in developing countries: land mines, child solders
1.5 million deaths in the conflict in Algeria
Means of control :
- How to fight are those who create wars and to know :
- case of expropriation of ealth in developed countries (oil, uranium...)
- put a stop on the ideological conflicts and racial hatred
- lproblems of nationalities most often unrecognized by national borders
- imperialist design of certain regimes or states, as explained nationalism (often disguised)
- put pressure on the armes dealers or manipulation of the great powers
The number of refugees around the world and that of the dispalced are increasing with the greatest number is found in countries of this development that increase yet the poverty of these countries.
World youth day :
To stop the wars in the world will never see the day
International Day of Persons with Disabilities: December 3
Reflections :
Reflections of upper management (UN, WHO ...)
UN, considering sanctions against countries and groups do not respect international conventions on the protection of children in armed conflict.
Personal Reflections:
The UN, as the WHO plan, but do not take decisions, pending decisions to be made for them by politicians.
It must remind its forums that in wars, victims are most often the living and the dead.
When the victims are alive, what will happen to their bodies ? NOTHING
Reflections of upper management (UN, WHO ...)
UN, considering sanctions against countries and groups do not respect international conventions on the protection of children in armed conflict.
Personal Reflections:
The UN, as the WHO plan, but do not take decisions, pending decisions to be made for them by politicians.
It must remind its forums that in wars, victims are most often the living and the dead.
When the victims are alive, what will happen to their bodies ? NOTHING
72 % of the planet covered under water
97% of available water is saline (sea) and not suitable for drinking
2% trapped as polar ice and in glaciers
1% suitable for consumption
Unsafe, polluted and untreated water for drinking and daily use causes 80% of diseases of the poor and developing countries.
Disparities in Water consumption liters/day/person
USA 300
Europe 177
Australia 57
Africa/Asia 10
2 billion persons depend only on rain water and have no access to drinking water.
Water wars
Fact sheets from WHO/TDR:
Choléra
Novembre 2008
Novembre 2008
Dengue et dengue hémorragiq
Mai 2008
Mai 2008
Epidemic in 70 countries
1.2 million persons infected each year
22000 deaths per year
It can affect the lives of 2.5 billion persons living in dengue infested areas. Man made disease, rapid urbanization, poor sanitation, lack of proper water resources, deforstation have contributed to breeding of mosquitoes in urban areas. There is no vaccine or antiviral treatment. Caused by Aedes mosquito infected with 4 types of dengue virus. Dengue hemorrhagic fever is a lethal complication of the disease.
Fievre de lassa
Avril 2005
Avril 2005
Filariose lymphatique
Septembre 2000
Septembre 2000
WHO web site info and image

Lymphatic filariasis is infection with the filarial worms, Wuchereria bancrofti, Brugia malayi or B. timori. These parasites are transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected mosquito and develop into adult worms in the lymphatic vessels, causing severe damage and swelling (lymphoedema). Elephantiasis – painful, disfiguring swelling of the legs and genital organs – is a classic sign of late-stage disease. Annual treatment of all individuals at risk with recommended anti-filarial drugs combination of either diethyl-carbamazine citrate (DEC) and albendazole, or ivermectin and albendazole; or the regular use of DEC fortified salt can prevent occurrence of new infection and disease. This disease can be eliminated


Leishmaniasis
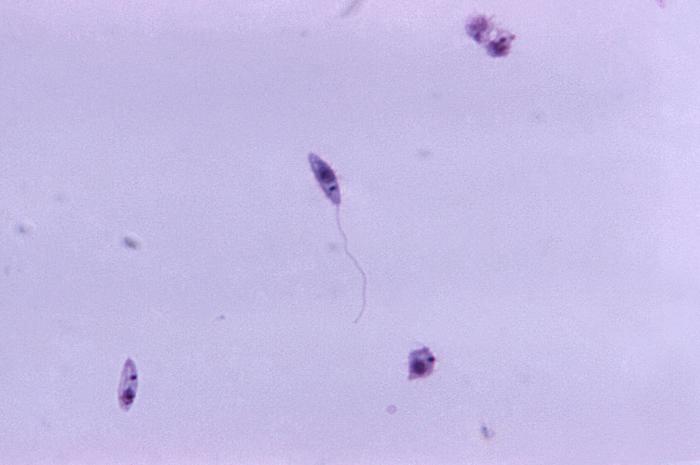
Sandflies infected with the parasite Leishmania transmit the protoza to humans. In cutaneous form skin ulcers form and leave a scar. Leprosy like symptoms in diffuse cutaneous form. High fatality rate in the Viceral form with high fever and weight loss and anemia (Kala Azar). New drug treatment marketed in India.
The Leishmania species protozoa are shown in the CDC PHIL 11704 photograph

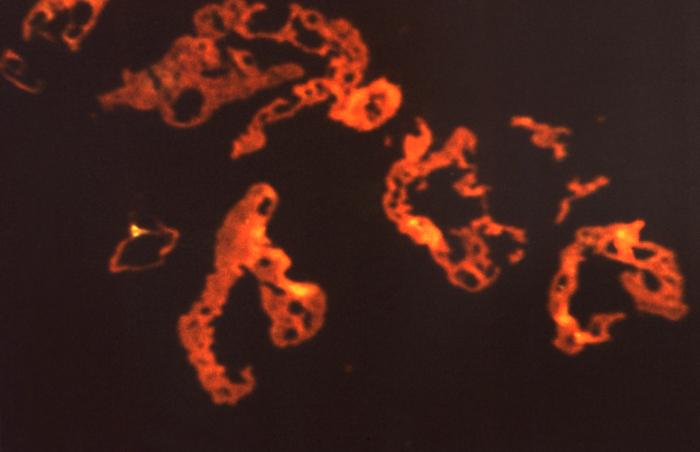
Schistosomiasis, or bilharzia, is a parasitic disease caused by trematode flatworms of the genus Schistosoma. In the body, the larvae develop into adult schistosomes, which live in the blood vessels. The females release eggs, some of which are passed out of the body in the urine or faeces.
In urinary schistosomiasis, there is progressive damage to the bladder, ureters and kidneys. In intestinal schistosomiasis, there is progressive enlargement of the liver and spleen, intestinal damage, and hypertension of the abdominal blood vessels.
Control of schistosomiasis is based on drug treatment, snail control, improved sanitation and health education.
CDC PHIL 11201
Schistosoma mansoni trematodes
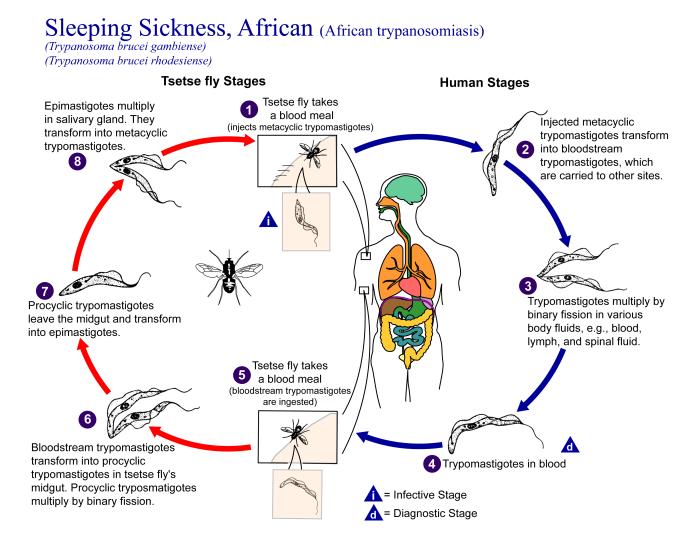
Human African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness is a widespread tropical disease that can be fatal if not treated. It is spread by the bite of an infected tsetse fly (Glossina Genus).
The tsetse fly bite erupts into a red sore and within a few weeks the person can experience fever, swollen lymph glands, aching muscles and joints, headaches and irritability.
In advanced stages, the disease attacks the central nervous system, causing changes in personality, alteration of the biological clock (the circadian rhythm), confusion, slurred speech, seizures, and difficulty walking and talking. These problems can develop over many years in the Gambiense form and some months in the Rhodesiense form; if not treated, the person will die.
Control of sleeping sickness is based on reduction of the reservoirs of infection by early diagnosis and control of tsetse flies.
CDC PHIL 3418 Life cycle of the parasite
Fièvre de la vallée du Rift
Septembre 2000
Septembre 2000
La lèpre
Octobre 2005
Octobre 2005
Le pian: une maladie oubliée
Janvier 2007
Janvier 2007
Maladies émergentes transmises par les aliments
Janvier 2002
Janvier 2002
ULCER BURULI
Updated
Sources, data and images cited and used are mainly from WHO, CDC, NIH or World Health Day related to the disease
Parasitic Diseases
- Ascariasis * (CDC, WHO
 , WHO-general
, WHO-general )
) - Ascaris lumbricoides * (CDC, WHO
 , WHO-general
, WHO-general )
) - Bilharzia (CDC, WHO
 , WHO-PPC
, WHO-PPC ) (see also Schistosomiasis)
) (see also Schistosomiasis) - Dracunculiasis (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Dracunculus medinensis (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Fasciola gigantica (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Fasciola hepatica (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Fascioliasis (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Guinea Worm Disease (CDC, WHO
 ) (see also Dracunculiasis)
) (see also Dracunculiasis) - Helminthiasis * (WHO
 , WHO-PPC
, WHO-PPC )
) - Hookworm * (CDC, WHO-general
 )
) - Lymphatic filariasis * (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Malaria ** (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Onchocerciasis ** (CDC, WHO
 )
) - River Blindness ** (CDC, WHO
 ) (see also Onchocerciasis)
) (see also Onchocerciasis) - Scabies * (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Schistosoma (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Schistosomiasis (CDC, WHO
 )
) - Soil transmitted helminths * (WHO
 , WHO-PPC
, WHO-PPC )
) - Trichuris trichuria (whipworm) * (CDC, WHO-general
 )
)
Global Health TV Show - November 2009
Tuesday, 1st December is World Aids Day. In this special program we talk to Dr Steve Patterson from Imperial College, London about his team's recent research in to the STEP vaccine trials in to HIV/AIDS with researchers from King's College London and Royal Holloway, Uni. of London.
Combating Neglected Tropical Diseases
Major Report on Child Vaccines
World Pneumonia Day
Tuesday, 1st December is World Aids Day. In this special program we talk to Dr Steve Patterson from Imperial College, London about his team's recent research in to the STEP vaccine trials in to HIV/AIDS with researchers from King's College London and Royal Holloway, Uni. of London.
Combating Neglected Tropical Diseases
Major Report on Child Vaccines
World Pneumonia Day
The proportion of disabled people is rising and now represents 1 billion people - 15% of ...
Unlocking the vast potential of people with disabilities
9 June 2011 -- The World report on disability, released today, reveals over a billion people with disabilities face significant barriers in their daily lives. The report encourages governments to increase efforts to enable access to mainstream health services among other things and invest in programmes to unlock the vast potential of people with disabilities.































Aucun commentaire:
Enregistrer un commentaire